- Basic theory of CT
- - What's inside the gantry ?
- - Data acquisition
- - Image reconstruction
- Variations is scanner design
- - Generation
- - Detector type
- - Number of Projections and detectors
- - Slip-ring scanning
 |
| basics of CT scanning |
 |
| basic principles of CT scanning |
 |
| back projection |
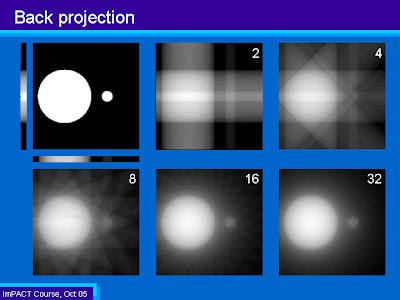 |
| ct scanning |
 |
| filtered back projection |
 |
| filtered back projection |
 | |
|
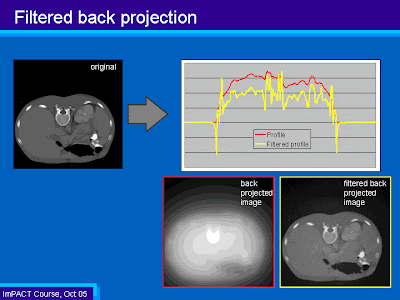 | |
|
 |
| re-binning fan beam data |
 |
Stop-start gantry |
 |
Slip rings |


.gif)



























0 التعليقات:
Post a Comment